pacman::p_load(sf, tmap, sfdep, tidyverse)
#keep tidyverse at the end for dependency checkingIn-Class Exercise 6: Choropleth Mapping
1.0 Overview
2.0 Setup
2.1 Installing and Loading the R Packages
2.2 The Data
Hunan, a geospatial data set in ESRI shapefile format, and
Hunan_2012, an attribute data set in csv format.
2.2.1 Import Geospatial Data
hunan <- st_read(dsn = "data/geospatial",
layer = "Hunan")Reading layer `Hunan' from data source
`/Users/shambhavigoenka/Desktop/School/Geo/IS415-GAA/in-class_ex/in-class_ex06/data/geospatial'
using driver `ESRI Shapefile'
Simple feature collection with 88 features and 7 fields
Geometry type: POLYGON
Dimension: XY
Bounding box: xmin: 108.7831 ymin: 24.6342 xmax: 114.2544 ymax: 30.12812
Geodetic CRS: WGS 842.2.2 Import attribute table
hunan2012 <- read_csv("data/aspatial/Hunan_2012.csv")2.2.3 Combine both data frames using left join
In order to retain the geospatial properties, the left data frame must be the sf data.frame(i.e. hunan)
hunan_GDPPC <- left_join(hunan,hunan2012)%>%
select(1:4, 7, 15) #name, id, name, engtype, 7 - county, 15 - gdppc2.2.3 Choropleth Map
tmap_mode("plot")
tm_shape(hunan_GDPPC) +
tm_fill("GDPPC",
style = "quantile",
palette = "Blues",
title = "GDPPC") +
tm_layout(main.title = "Distribution of GDP per capita by district, Hunan Province",
main.title.position = "center",
main.title.size = 1.2,
legend.height = 0.45,
legend.width = 0.35,
frame = TRUE) +
tm_borders(alpha = 0.5) +
# tm_text("NAME_3", size=0.5) +
tm_compass(type = "8star", size = 2) +
tm_scale_bar() + #decimal degree projection turns into km using great circle calculation
tm_grid(alpha = 0.2)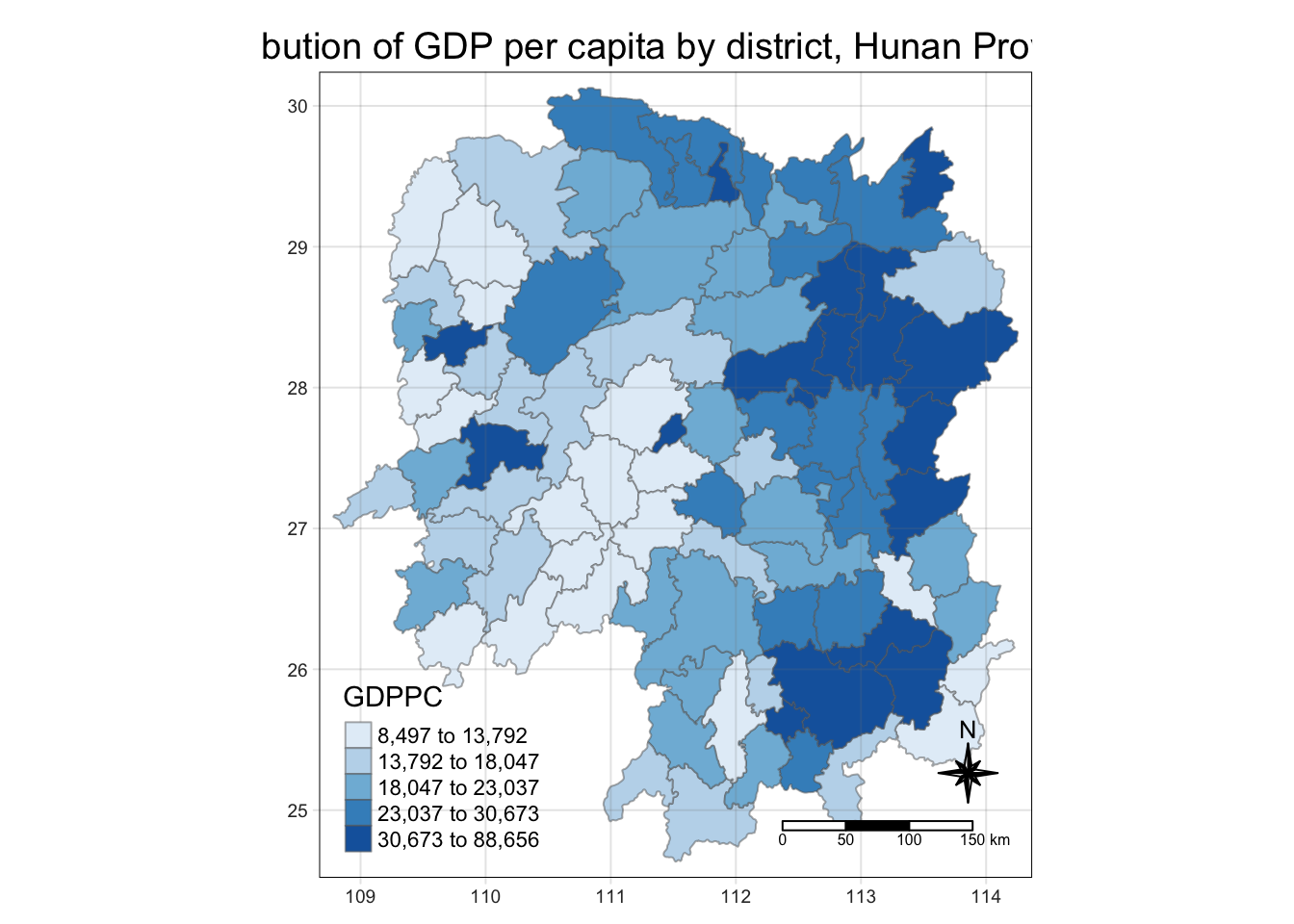
3.0 Identify area neighbors
3.1 Contiguity Spatial Weights
Redundant in later steps = 4.1
3.1.1 Derive neighbor’s list using Queen’s method
# -- st version
nb_queen <- hunan_GDPPC %>%
mutate(nb = st_contiguity(geometry), #default is queen
.before = 1) #place as first column
#wm_q <- poly2nd(hunan_GDPPC, queen = TRUE) -- sp version3.1.2 Derive neighbor’s list using Rook’s method
nb_rook <- hunan_GDPPC %>%
mutate(nb = st_contiguity(geometry), #default is queen
queen = FALSE,
.before = 1) #place as first column3.1.3 Identifying higher order neighbors
Queen Method
nb2_queen <- hunan_GDPPC %>%
mutate(nb = st_contiguity(geometry),
nb2 = st_nb_lag_cumul(nb, 2),
.before = 1)4.0 K-nearest neighbors method
4.1 Contiguity Spatial Weights
4.1.1 Derive neighbor’s list using Queen’s method
wm_q <- hunan_GDPPC %>%
mutate(nb = st_contiguity(geometry),
wt = st_weights(nb,
style = "W"),
.before = 1) 4.1.2 Derive neighbor’s list using Rook’s method
wm_r <- hunan %>%
mutate(nb = st_contiguity(geometry,
queen = FALSE),
wt = st_weights(nb),
.before = 1) 5.0 Distance-based Weights
5.1 Distance band method
Fixed distance criterion - lower = 0, upper = whatever
geo <- sf::st_geometry(hunan_GDPPC)
nb <- st_knn(geo, longlat = TRUE)
dists <- unlist(st_nb_dists(geo, nb))summary(dists) Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
21.56 29.11 36.89 37.34 43.21 65.80 Maximum nearest neighbor distance is 65.80km so threshold of 66km means there will be at least one neighbor
wm_fd <- hunan_GDPPC %>%
mutate(nb = st_dist_band(geometry,
upper = 66),
wt = st_weights(nb),
.before = 1)5.2 Adaptive Distance Method
wm_ad <- hunan_GDPPC %>%
mutate(nb = st_knn(geometry,
k=8),
wt = st_weights(nb),
.before = 1)5.3 Inverse Distance Method
wm_idw <- hunan_GDPPC %>%
mutate(nb = st_contiguity(geometry),
wts = st_inverse_distance(nb, geometry,
scale = 1,
alpha = 1),
.before = 1)